Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is an important part of the wave of innovations changing the way we do business today. Basically speaking, cloud computing refers to the delivery of various computing services such as storage, networking, servers, analytics, databases, and software over the Internet, all of which together is called “the cloud”. Cloud computing is a way to access flexible resources, economies of scale, and faster innovation. Figuratively speaking, it’s all floating around up there in the cloud waiting for you to take advantage of it!
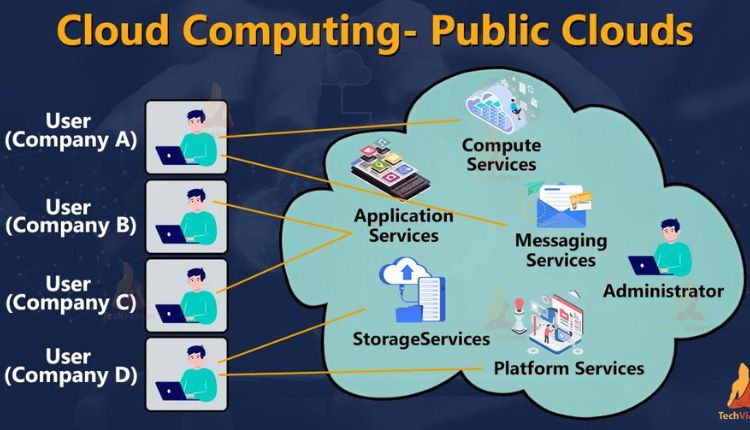
There are several kinds of clouds, and today we will focus on the public cloud, a selection of virtual resources that are developed from hardware belonging to a third-party company that are provisioned and allocated automatically through a self-service interface to multiple clients. Many notable companies have created a public cloud, such as Azure Arc, as a straightforward method for handling unexpected demand fluctuations when scaling out workloads. In general, public clouds aren’t used as a stand-alone infrastructure solution, they are part of a stable of environments that promote wider availability for infrastructure, services, and applications, while offering lower costs, higher security, and better performance.
What is it that makes a cloud public?
Management – The public cloud provider will maintain the operations of the hardware powering the cloud, support the network, and manage all of the software’s virtualisation.
Resource Allocation – Those tenants who are outside the provider’s protective firewall can all share virtual resources and cloud services from the provider’s set of software, infrastructure, and platforms.
Use Agreements – The private cloud’s resources are distributed on an as-needed basis, with pay-as-you-go models as components. Some clients such as research institutions are granted access to, and are able to use public clouds for free.
How can I use a public cloud?
A public cloud works on a fairly simple model. When a client requires more resources, services, or platforms, they pay their public cloud service provider by the byte or by the hour to have access to the things they require in the time frame that they are necessary. The hardware owned by the vendor virtualizes infrastructure, storage, cloud-based applications, and raw processing power into data lakes that are organized by the automation software and management to be shared with the client over the internet or a dedicated network connection.
How are public clouds secured?
These days security is of the utmost concern for anyone engaged in online activities, including public clouds. A public cloud plays host to critical workloads and sensitive data, so keeping them safe is a high priority. While the public cloud providers implement a variety of security technologies and services, the cloud’s safety also requires diligence and care on the part of the clients.
Responsibility is shared between the public cloud and its users for the security duties based on a framework that designates the particular security and accountability aspects for both. For example, the cloud provider secures the infrastructure, but it’s the responsibility of the user to employ security tools and firewalls to help maintain proper security for workloads and data.
The adoption of the public cloud continues to grow as providers offer more and more services and higher levels of support. See you in the clouds!







